Structure of a Monocotyledonous Maize Seed
Structure of a Monocotyledonous Maize Seed: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Perisperm and Structure of a Monocot Seed
Important Questions on Structure of a Monocotyledonous Maize Seed
Aleurone layer of seed of maize is specifically rich in:
Give some examples of seeds that show perisperm.
Identify the correct match for the Maize grain from the given options
Perisperm present in the seeds of:
Which is true for Perisperm?
Generally monocotyledonous seeds are (A) but some as in (B) are (C).
Mark odd one out with respect to maize grain.
Cotyledon of maize grain is called:-
What are the ploidy of labelled structure , in given diagram of maize seed?
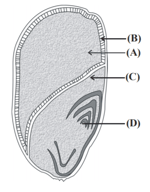
Persistent nucellus in seed :-
Perisperm can be observed in seeds of:-
Occasionally, in some seeds such as black pepper, beet and castor, remnants of nucellus are also persistent. This residual, persistent nucellus is called
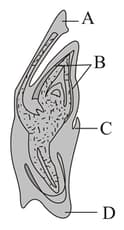
In above diagram represents :
Endosperm of angiosperm, has analogy with :-
What is persistent nucellus known as and where is it found?
In the given diagram of V.S. of maize grain, identify the labelled parts and choose the correct option.
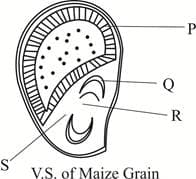
In Zea mays, the outermost layer of endosperm is rich in proteins. This layer is called as ______
In maize seed, the scutellum is considered cotyledon as it
Which of these are the examples of seeds that show perisperm?
_____ is a nutritive tissue that surrounds the embryo of a seed.
